The Value of Diamonds
The value of diamonds is determined chiefly by their size, purity, colour, freedom from flaws or stains, and the skill with which they are manufactured. Their weight is reckoned by the carat, of four diamond grains, originally an Indian weight.
In England the carat is estimated as = 3·174 grains troy; but it varies in different places, being, according to Schrauf, in Amsterdam = 205·70 milligrammes, in Florence = 197·20, in London = 205·409, in Madras = 207·353, in Paris = 205·50, and in Vienna = 206·13.
The usual rule is that the value of the stone increases with the square of the weight in carats, and assuming £8 or £10 as the value of a cut brilliant of first quality in water and shape, weighing 1 carat, a similar stone of 2 carats would be worth four (2 x 2) times £8 or £10, i.e. £32 to £40; one of 3 carats nine (3 x 3) times, or £72 to £90; and so in proportion.
Fine brilliants, however, of the sizes most in demand sell much higher, or from £12 to £20 or more the first carat; whilst roses and tables are of considerably smaller, value, and rough or uncut diamonds, generally sold in lots, fetch only about £2 or even less, the value being further diminished in all cases where the stones are "of colour," that is milky or tinted, or imperfect in other respects.
Still more important is the state of supply and demand, especially for the largest and most valuable stone, for which there are often very few purchasers, and their price is thus lower than the rule would imply. Even political events affect the price by bringing many into the market, as at the time of the first French Revolution.
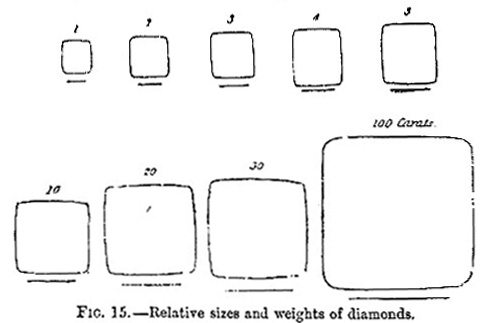
In 1873 Cape diamonds were stated to be worth -- yellows under 5 carats, 40s. to 50s.; above that weight, £3 to £4 per carat; pure white stones under 5 carats, £3 to £4 ; and above 5 carats, £4 to £7, or more according to form or luster. Fig. 15 shows the size of set stones round the girdle, the line indicating their depth, and the numerals the number of carats they may be expected to weigh.
Read the rest of this article:
Diamond - Table of Contents